Vue Router路由
安装
直接下载 / CDN
https://unpkg.com/vue-router/dist/vue-router.js
在 Vue 后面加载 vue-router,它会自动安装的:
<script src="/path/to/vue.js"></script>
<script src="/path/to/vue-router.js"></script>
NPM
npm install vue-router
如果在一个模块化工程中使用它,必须要通过 Vue.use() 明确地安装路由功能:
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
起步
用 Vue.js + Vue Router 创建单页应用,是非常简单的。使用 Vue.js ,我们已经可以通过组合组件来组成应用程序,当你要把 Vue Router 添加进来,我们需要做的是,将组件 (components) 映射到路由 (routes),然后告诉 Vue Router 在哪里渲染它们。下面是个基本例子:
HTML
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue-router/dist/vue-router.js"></script>
<div id="app">
<h1>Hello App!</h1>
<p>
<!-- 使用 router-link 组件来导航. -->
<!-- 通过传入 `to` 属性指定链接. -->
<!-- <router-link> 默认会被渲染成一个 `<a>` 标签 -->
<router-link to="/foo">Go to Foo</router-link>
<router-link to="/bar">Go to Bar</router-link>
</p>
<!-- 路由出口 -->
<!-- 路由匹配到的组件将渲染在这里 -->
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
// 0. 如果使用模块化机制编程,导入Vue和VueRouter,要调用 Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 1. 定义 (路由) 组件。
// 可以从其他文件 import 进来
const Foo = { template: '<div>foo</div>' }
const Bar = { template: '<div>bar</div>' }
// 2. 定义路由
// 每个路由应该映射一个组件。 其中"component" 可以是
// 通过 Vue.extend() 创建的组件构造器,
// 或者,只是一个组件配置对象。
// 我们晚点再讨论嵌套路由。
const routes = [
{ path: '/foo', component: Foo },
{ path: '/bar', component: Bar }
]
// 3. 创建 router 实例,然后传 `routes` 配置
// 你还可以传别的配置参数, 不过先这么简单着吧。
const router = new VueRouter({
routes // (缩写) 相当于 routes: routes
})
// 4. 创建和挂载根实例。
// 记得要通过 router 配置参数注入路由,
// 从而让整个应用都有路由功能
const app = new Vue({
router
}).$mount('#app')
// 现在,应用已经启动了!
通过注入路由器,我们可以在任何组件内通过 this.$router 访问路由器,也可以通过 this.$route 访问当前路由:
// Home.vue
export default {
computed: {
username () {
// 我们很快就会看到 `params` 是什么
return this.$route.params.username
}
},
methods: {
goBack () {
window.history.length > 1
? this.$router.go(-1)
: this.$router.push('/')
}
}
}
提示
该文档通篇都常使用 router 实例。留意一下 this.$router 和 router 使用起来完全一样。我们使用 this.$router 的原因是我们并不想在每个独立需要封装路由的组件中都导入路由。
要注意,当 <router-link> 对应的路由匹配成功,将自动设置 class 属性值 .router-link-active。查看 API 文档 学习更多相关内容。
动态路由匹配
我们经常需要把某种模式匹配到的所有路由,全都映射到同个组件。例如,我们有一个 User 组件,对于所有 ID 各不相同的用户,都要使用这个组件来渲染。那么,我们可以在 vue-router 的路由路径中使用“动态路径参数”(dynamic segment) 来达到这个效果:
const User = {
template: '<div>User</div>'
}
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
// 动态路径参数 以冒号开头
{ path: '/user/:id', component: User }
]
})
现在呢,像 /user/foo 和 /user/bar 都将映射到相同的路由。
一个“路径参数”使用冒号 : 标记。当匹配到一个路由时,参数值会被设置到 this.$route.params,可以在每个组件内使用。于是,我们可以更新 User 的模板,输出当前用户的 ID:
const User = {
template: '<div>User {{ $route.params.id }}</div>'
}
你可以在一个路由中设置多段“路径参数”,对应的值都会设置到 $route.params 中。例如:
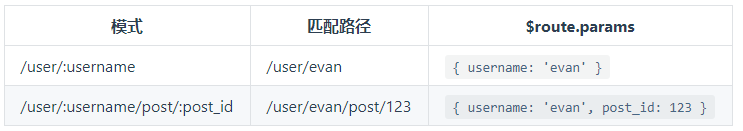
除了 $route.params 外,$route 对象还提供了其它有用的信息,例如,$route.query (如果 URL 中有查询参数)、$route.hash 等等。
响应路由参数的变化
提醒一下,当使用路由参数时,例如从 /user/foo 导航到 /user/bar,原来的组件实例会被复用。因为两个路由都渲染同个组件,比起销毁再创建,复用则显得更加高效。不过,这也意味着组件的生命周期钩子不会再被调用。
复用组件时,想对路由参数的变化作出响应的话,你可以简单地 watch (监测变化) $route 对象:
const User = {
template: '...',
watch: {
'$route' (to, from) {
// 对路由变化作出响应...
}
}
}
或者使用 2.2 中引入的 beforeRouteUpdate 守卫:
const User = {
template: '...',
beforeRouteUpdate (to, from, next) {
// don't forget to call next()
}
}
嵌套路由
实际生活中的应用界面,通常由多层嵌套的组件组合而成。同样地,URL 中各段动态路径也按某种结构对应嵌套的各层组件,例如:
/user/foo/profile /user/foo/posts
+------------------+ +-----------------+
| User | | User |
| +--------------+ | | +-------------+ |
| | Profile | | +------------> | | Posts | |
| | | | | | | |
| +--------------+ | | +-------------+ |
+------------------+ +-----------------+
借助 vue-router,使用嵌套路由配置,就可以很简单地表达这种关系。
接着上节创建的 app:
<div id="app">
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
const User = {
template: '<div>User {{ $route.params.id }}</div>'
}
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/user/:id', component: User }
]
})
这里的 <router-view> 是最顶层的出口,渲染最高级路由匹配到的组件。同样地,一个被渲染组件同样可以包含自己的嵌套 <router-view>。例如,在 User 组件的模板添加一个 <router-view>:
const User = {
template: `
<div class="user">
<h2>User {{ $route.params.id }}</h2>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
`
}
要在嵌套的出口中渲染组件,需要在 VueRouter 的参数中使用 children 配置:
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/user/:id', component: User,
children: [
{
// 当 /user/:id/profile 匹配成功,
// UserProfile 会被渲染在 User 的 <router-view> 中
path: 'profile',
component: UserProfile
},
{
// 当 /user/:id/posts 匹配成功
// UserPosts 会被渲染在 User 的 <router-view> 中
path: 'posts',
component: UserPosts
}
]
}
]
})
注意
以 / 开头的嵌套路径会被当作根路径。 这让你充分的使用嵌套组件而无须设置嵌套的路径。
你会发现,children 配置就是像 routes 配置一样的路由配置数组,所以呢,你可以嵌套多层路由。
此时,基于上面的配置,当你访问 /user/foo 时,User 的出口是不会渲染任何东西,这是因为没有匹配到合适的子路由。如果你想要渲染点什么,可以提供一个 空的 子路由:
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path: '/user/:id', component: User,
children: [
// 当 /user/:id 匹配成功,
// UserHome 会被渲染在 User 的 <router-view> 中
{ path: '', component: UserHome },
// ...其他子路由
]
}
]
})
编程式的导航
除了使用 <router-link> 创建 a 标签来定义导航链接,我们还可以借助 router 的实例方法,通过编写代码来实现。
router.push(location, onComplete?, onAbort?)
注意
在 Vue 实例内部,你可以通过 $router 访问路由实例。因此你可以调用 this.$router.push。
想要导航到不同的 URL,则使用 router.push 方法。这个方法会向 history 栈添加一个新的记录,所以,当用户点击浏览器后退按钮时,则回到之前的 URL。
当你点击 <router-link> 时,这个方法会在内部调用,所以说,点击 <router-link :to="..."> 等同于调用 router.push(...)。
该方法的参数可以是一个字符串路径,或者一个描述地址的对象。例如:
// 字符串
router.push('home')
// 对象
router.push({ path: 'home' })
// 命名的路由
router.push({ name: 'user', params: { userId: 123 }})
// 带查询参数,变成 /register?plan=private
router.push({ path: 'register', query: { plan: 'private' }})
注意
如果提供了 path,params 会被忽略,上述例子中的 query 并不属于这种情况。取而代之的是下面例子的做法,你需要提供路由的 name 或手写完整的带有参数的 path:
const userId = 123
router.push({ name: 'user', params: { userId }}) // -> /user/123
router.push({ path: `/user/${userId}` }) // -> /user/123
// 这里的 params 不生效
router.push({ path: '/user', params: { userId }}) // -> /user
router.replace(location, onComplete?, onAbort?)
跟 router.push 很像,唯一的不同就是,它不会向 history 添加新记录,而是跟它的方法名一样 —— 替换掉当前的 history 记录。
router.go(n)
这个方法的参数是一个整数,意思是在 history 记录中向前或者后退多少步,类似 window.history.go(n)。
// 在浏览器记录中前进一步,等同于 history.forward()
router.go(1)
// 后退一步记录,等同于 history.back()
router.go(-1)
// 前进 3 步记录
router.go(3)
// 如果 history 记录不够用,那就默默地失败呗
router.go(-100)
router.go(100)
命名路由
有时候,通过一个名称来标识一个路由显得更方便一些,特别是在链接一个路由,或者是执行一些跳转的时候。你可以在创建 Router 实例的时候,在 routes 配置中给某个路由设置名称。
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path: '/user/:userId',
name: 'user',
component: User
}
]
})
要链接到一个命名路由,可以给 router-link 的 to 属性传一个对象:
<router-link :to="{ name: 'user', params: { userId: 123 }}">User</router-link>
这跟代码调用 router.push() 是一回事:
router.push({ name: 'user', params: { userId: 123 }})
这两种方式都会把路由导航到 /user/123 路径。
重定向和别名
重定向
重定向也是通过 routes 配置来完成,下面例子是从 /a 重定向到 /b:
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/a', redirect: '/b' }
]
})
重定向的目标也可以是一个命名的路由:
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/a', redirect: { name: 'foo' }}
]
})
甚至是一个方法,动态返回重定向目标:
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/a', redirect: to => {
// 方法接收 目标路由 作为参数
// return 重定向的 字符串路径/路径对象
}}
]
})
别名
“重定向”的意思是,当用户访问 /a时,URL将会被替换成 /b,然后匹配路由为 /b,那么“别名”又是什么呢?
/a 的别名是 /b,意味着,当用户访问 /b 时,URL 会保持为 /b,但是路由匹配则为 /a,就像用户访问 /a 一样。
上面对应的路由配置为:
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/a', component: A, alias: '/b' }
]
})
“别名”的功能让你可以自由地将 UI 结构映射到任意的 URL,而不是受限于配置的嵌套路由结构。
路由组件传参
在组件中使用 $route 会使之与其对应路由形成高度耦合,从而使组件只能在某些特定的 URL 上使用,限制了其灵活性。
使用 props 将组件和路由解耦:
取代与 $route 的耦合
const User = {
template: '<div>User {{ $route.params.id }}</div>'
}
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/user/:id', component: User }
]
})
通过 props 解耦
const User = {
props: ['id'],
template: '<div>User {{ id }}</div>'
}
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/user/:id', component: User, props: true },
// 对于包含命名视图的路由,你必须分别为每个命名视图添加 `props` 选项:
{
path: '/user/:id',
components: { default: User, sidebar: Sidebar },
props: { default: true, sidebar: false }
}
]
})
这样你便可以在任何地方使用该组件,使得该组件更易于重用和测试。
布尔模式
如果 props 被设置为 true,route.params 将会被设置为组件属性。
HTML5 History 模式
vue-router 默认 hash 模式 —— 使用 URL 的 hash 来模拟一个完整的 URL,于是当 URL 改变时,页面不会重新加载。
如果不想要很丑的 hash,我们可以用路由的 history 模式,这种模式充分利用 history.pushState API 来完成 URL 跳转而无须重新加载页面。
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'history',
routes: [...]
})
当你使用 history 模式时,URL 就像正常的 url,例如 http://yoursite.com/user/id,也好看!
不过这种模式要玩好,还需要后台配置支持。因为我们的应用是个单页客户端应用,如果后台没有正确的配置,当用户在浏览器直接访问 http://oursite.com/user/id 就会返回 404,这就不好看了。
后端配置例子
Apache
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteRule ^index\.html$ - [L]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule . /index.html [L]
</IfModule>
nginx
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;
}
原生 Node.js
const http = require('http')
const fs = require('fs')
const httpPort = 80
http.createServer((req, res) => {
fs.readFile('index.htm', 'utf-8', (err, content) => {
if (err) {
console.log('We cannot open "index.htm" file.')
}
res.writeHead(200, {
'Content-Type': 'text/html; charset=utf-8'
})
res.end(content)
})
}).listen(httpPort, () => {
console.log('Server listening on: http://localhost:%s', httpPort)
})
IIS
- 安装 IIS UrlRewrite
- 在你的网站根目录中创建一个
web.config文件,内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<rewrite>
<rules>
<rule name="Handle History Mode and custom 404/500" stopProcessing="true">
<match url="(.*)" />
<conditions logicalGrouping="MatchAll">
<add input="{REQUEST_FILENAME}" matchType="IsFile" negate="true" />
<add input="{REQUEST_FILENAME}" matchType="IsDirectory" negate="true" />
</conditions>
<action type="Rewrite" url="/" />
</rule>
</rules>
</rewrite>
</system.webServer>
</configuration>
警告
给个警告,因为这么做以后,你的服务器就不再返回 404 错误页面,因为对于所有路径都会返回 index.html 文件。为了避免这种情况,你应该在 Vue 应用里面覆盖所有的路由情况,然后在给出一个 404 页面。
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'history',
routes: [
{ path: '*', component: NotFoundComponent }
]
})
路由懒加载
当打包构建应用时,Javascript 包会变得非常大,影响页面加载。如果我们能把不同路由对应的组件分割成不同的代码块,然后当路由被访问的时候才加载对应组件,这样就更加高效了。
结合 Vue 的异步组件和 Webpack 的代码分割功能,轻松实现路由组件的懒加载。
首先,可以将异步组件定义为返回一个 Promise 的工厂函数 (该函数返回的 Promise 应该 resolve 组件本身):
const Foo = () => Promise.resolve({ /* 组件定义对象 */ })
第二,在 Webpack 2 中,我们可以使用动态 import语法来定义代码分块点 (split point):
import('./Foo.vue') // 返回 Promise
注意
如果您使用的是 Babel,你将需要添加 syntax-dynamic-import 插件,才能使 Babel 可以正确地解析语法。
结合这两者,这就是如何定义一个能够被 Webpack 自动代码分割的异步组件。
const Foo = () => import('./Foo.vue')
在路由配置中什么都不需要改变,只需要像往常一样使用 Foo:
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/foo', component: Foo }
]
})
把组件按组分块
有时候我们想把某个路由下的所有组件都打包在同个异步块 (chunk) 中。只需要使用 命名 chunk,一个特殊的注释语法来提供 chunk name (需要 Webpack > 2.4)。
const Foo = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "group-foo" */ './Foo.vue')
const Bar = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "group-foo" */ './Bar.vue')
const Baz = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "group-foo" */ './Baz.vue')